Doubly Linked List
"""
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list
"""
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.previous = None
self.next = None
def __str__(self):
return f"{self.data}"
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
def __iter__(self):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.insert_at_head('b')
>>> linked_list.insert_at_head('a')
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail('c')
>>> tuple(linked_list)
('a', 'b', 'c')
"""
node = self.head
while node:
yield node.data
node = node.next
def __str__(self):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail('a')
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail('b')
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail('c')
>>> str(linked_list)
'a->b->c'
"""
return "->".join([str(item) for item in self])
def __len__(self):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> for i in range(0, 5):
... linked_list.insert_at_nth(i, i + 1)
>>> len(linked_list) == 5
True
"""
return sum(1 for _ in self)
def insert_at_head(self, data):
self.insert_at_nth(0, data)
def insert_at_tail(self, data):
self.insert_at_nth(len(self), data)
def insert_at_nth(self, index: int, data):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(-1, 666)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(1, 666)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(0, 2)
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(0, 1)
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(2, 4)
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(2, 3)
>>> str(linked_list)
'1->2->3->4'
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(5, 5)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
"""
length = len(self)
if not 0 <= index <= length:
raise IndexError("list index out of range")
new_node = Node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = self.tail = new_node
elif index == 0:
self.head.previous = new_node
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
elif index == length:
self.tail.next = new_node
new_node.previous = self.tail
self.tail = new_node
else:
temp = self.head
for _ in range(index):
temp = temp.next
temp.previous.next = new_node
new_node.previous = temp.previous
new_node.next = temp
temp.previous = new_node
def delete_head(self):
return self.delete_at_nth(0)
def delete_tail(self):
return self.delete_at_nth(len(self) - 1)
def delete_at_nth(self, index: int):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
>>> for i in range(0, 5):
... linked_list.insert_at_nth(i, i + 1)
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(0) == 1
True
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(3) == 5
True
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(1) == 3
True
>>> str(linked_list)
'2->4'
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(2)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
"""
length = len(self)
if not 0 <= index <= length - 1:
raise IndexError("list index out of range")
delete_node = self.head # default first node
if length == 1:
self.head = self.tail = None
elif index == 0:
self.head = self.head.next
self.head.previous = None
elif index == length - 1:
delete_node = self.tail
self.tail = self.tail.previous
self.tail.next = None
else:
temp = self.head
for _ in range(index):
temp = temp.next
delete_node = temp
temp.next.previous = temp.previous
temp.previous.next = temp.next
return delete_node.data
def delete(self, data) -> str:
current = self.head
while current.data != data: # Find the position to delete
if current.next:
current = current.next
else: # We have reached the end an no value matches
raise ValueError("No data matching given value")
if current == self.head:
self.delete_head()
elif current == self.tail:
self.delete_tail()
else: # Before: 1 <--> 2(current) <--> 3
current.previous.next = current.next # 1 --> 3
current.next.previous = current.previous # 1 <--> 3
return data
def is_empty(self):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.is_empty()
True
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail(1)
>>> linked_list.is_empty()
False
"""
return len(self) == 0
def test_doubly_linked_list() -> None:
"""
>>> test_doubly_linked_list()
"""
linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
assert linked_list.is_empty() is True
assert str(linked_list) == ""
try:
linked_list.delete_head()
raise AssertionError # This should not happen.
except IndexError:
assert True # This should happen.
try:
linked_list.delete_tail()
raise AssertionError # This should not happen.
except IndexError:
assert True # This should happen.
for i in range(10):
assert len(linked_list) == i
linked_list.insert_at_nth(i, i + 1)
assert str(linked_list) == "->".join(str(i) for i in range(1, 11))
linked_list.insert_at_head(0)
linked_list.insert_at_tail(11)
assert str(linked_list) == "->".join(str(i) for i in range(12))
assert linked_list.delete_head() == 0
assert linked_list.delete_at_nth(9) == 10
assert linked_list.delete_tail() == 11
assert len(linked_list) == 9
assert str(linked_list) == "->".join(str(i) for i in range(1, 10))
if __name__ == "__main__":
from doctest import testmod
testmod()
Acerca de este algoritmo
Singly Linked List es una estructura de datos lineal y conectada formada por nodos. Cada nodo se compone de una variable 'data' donde se almacena su contenido y un puntero al siguiente nodo de la lista. La lista vinculada tiene un puntero al primer elemento de esta secuencia de nodos y también puede tener otro puntero al último nodo para realizar operaciones en el extremo lejano menos lento. También puede almacenar una variable 'length' para almacenar la longitud total.
Una lista vinculada doblemente (DLL)** contiene un puntero adicional, normalmente denominado puntero anterior, junto con el puntero siguiente y los datos que están allí en la lista vinculada individualmente.
Ventajas sobre la lista vinculada individualmente
- Un archivo DLL se puede atravesar tanto en dirección hacia delante como hacia atrás.
- La operación de eliminación en DLL es más eficaz si se da puntero al nodo que se va a eliminar.
- Podemos insertar rápidamente un nuevo nodo antes de un nodo determinado.
En la lista vinculada individualmente, para eliminar un nodo, se necesita puntero al nodo anterior. Para obtener este nodo anterior, a veces se atraviesa la lista. En DLL, podemos obtener el nodo anterior mediante el puntero anterior.
Desventajas sobre la lista de vinculados individualmente
- Cada nodo de DLL requiere espacio adicional para un puntero anterior. Sin embargo, es posible implementar DLL con un solo puntero (Consulte esto y esto).
- Todas las operaciones requieren un puntero adicional anterior para ser mantenido. Por ejemplo, en la inserción, necesitamos modificar punteros anteriores junto con punteros siguientes. Por ejemplo, en las siguientes funciones para las inserciones en diferentes posiciones, necesitamos 1 o 2 pasos adicionales para establecer el puntero anterior.
Complejidad temporal
| Operación | Promedio | Peor |
|---|---|---|
| Acceso | Ḥ(n) | O(n) |
| Buscar | Ḥ(n) | O(n) |
| de inserción Θ(1) | O(1) | |
| de eliminación Θ(1) | O(1) |
Ejemplo
class LinkedList {
Node head; // Pointer to the first element
Node tail; // Optional. Points to the last element
int length; // Optional
class Node {
int data; // Node data. Can be int, string, float, templates, etc
Node next; // Pointer to the next node on the list
Node prev;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// Asignar el nodo al frente de la lista
public void push(int new_data) {
/* 1. Asignar nodo.
* 2. Ponga los datos. */
Node new_Node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Haga el siguiente de nuevo nodo como cabeza y anterior como NULL. */
new_Node.next = head;
new_Node.prev = null;
/* 4. Cambie el nodo principal anterior a nuevo nodo. */
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_Node;
/* 5. Mueva la cabeza para apuntar al nuevo nodo. */
head = new_Node;
}
/* Dado un nodo como prev_node, inserte un nuevo nodo después del nodo dado. */
public void InsertAfter(Node prev_Node, int new_data) {
/* 1. Comprobar si el prev_node dado es NULL. */
if (prev_Node == null) {
System.out.println("The given previous node cannot be NULL ");
return;
}
/* 1. Asignar nodo.
* 2. Ponga los datos. */
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 4. Haga el siguiente de nuevo nodo como el siguiente de prev_node. */
new_node.next = prev_Node.next;
/* 5. Haz el siguiente de prev_node como new_node. */
prev_Node.next = new_node;
/* 6. Haga prev_node como antes de new_node. */
new_node.prev = prev_Node;
/* 7. Cambie el anterior del siguiente nodo de new_node. */
if (new_node.next != null)
new_node.next.prev = new_node;
}
}
Adición de nodos en frente
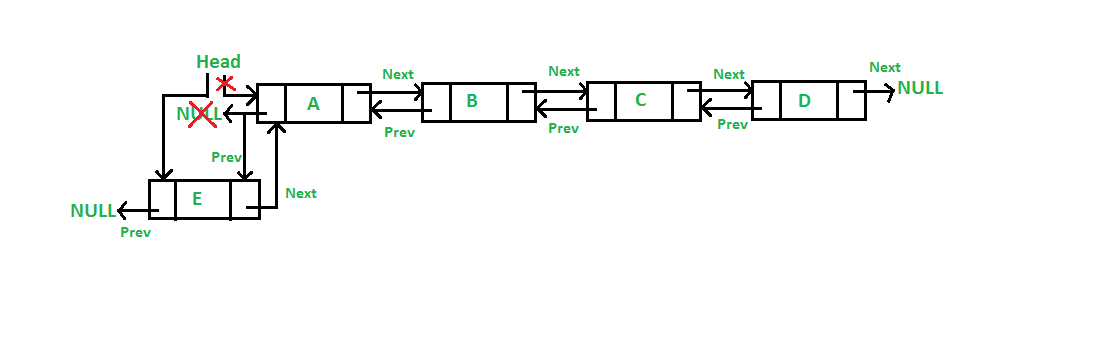
Agregue un nodo después de un nodo determinado

Explicación de vídeo
Un vídeo CS50 explicando la Estructura de Datos de la Lista Doblemente Vinculada